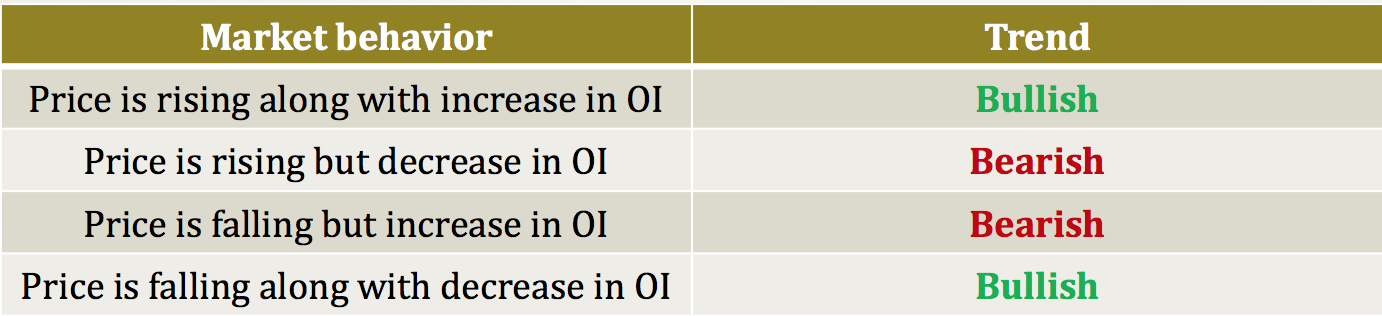
The greater a firm degree of operating leverage, the less its EBIT will vary with fluctuations in sales. The greater a firm degree of operating leverage, the more its EBIT will vary with respect to fluctuations in sales. The EBIT level is adjusted by subtracting the interest payments and the before-tax preferred stock dividends and then adjusting this figure for the tax effect. To put this amount on a per share basis, we divide by the number of common shares for each financing plan. When earnings before interest and taxes exceed the fixed obligations, favorable leverage occurs; when fixed obligations exceed earnings before interest and taxes, unfavorable leverage occurs.

From the financial point of view, leverage refers to furnish the ability to use fixed cost assets or funds to increase the return to its shareholders. EPSEarnings Per Share is a key financial metric that investors use to assess a company’s performance and profitability before investing. It is calculated by dividing total earnings or total net income by the total number of outstanding shares.
So, from the above analysis, the financial leverage value will be2.5. Note that this is only quasi-isotropic in the plane of the laminate – “in-plane quasi-isotropic”. In the “z” or top-to-bottom direction, the laminate properties are based largely on the resin matrix, because there are no z-axis fibers.
Examples of Financial Leverage Formula (With Excel Template)
Thus, it explains the degree of business risk complexion the firm. Financial leverage measures change in earning before tax on account of change in operating profits (i.e., EBIT). Both these leverages are closely concerned with the firm’s capability of meeting its fixed costs . In case both the leverages are combined, the result will depict the effect of change in sales level on the earning before tax . It is to be remembered that operating leverage occurs only when fixed costs are to be met, regardless of sales volume. Financial leverage results from the presence of fixed financial charges in the firm’s income stream.
Feel free to think of it as “resin” and “fiber” if that sounds more obvious – because that’s what you’ll call them when building stuff. For banks, the tier 1 leverage ratio is most commonly used by regulators. It is helpful to know how operating profit would change with a given change in units produced. There are three types of leverages, such as- Operating leverage, and Financial leverage. The higher the value of DFL, the higher will be financial leverage. The uses financial leverage to make decisions in the liability side of the Balance Sheet.
- Instead of calculating the percentage changes in output and EBIT, we can look at per unit data as given in Table 1 and calculate the degree of operating leverage at a level of output.
- Times interest earned , also known as a fixed-charge coverage ratio, is a variation of the interest coverage ratio.
- These costs remain constant irrespective of the amount of operating profits.
- This shows the point at which comparative methods of financing will yield the same results in earnings per share.
- For selection of Investment projects – A company should be careful while selecting investment projects.
- This directionality can make a composite much stronger in the direction of the fiber – while only about as strong as the resin in the other directions.
However when there is preference dividend as well, then it is better to use the first formula. This is because while interest expenses are tax deductible, preference dividend is not tax deductible in nature. Hence earnings available to equity shareholders get reduced further by the amount of preference dividend which is fixed.
David has helped thousands of clients improve their accounting and financial systems, create budgets, and minimize their taxes. The use of Long Term Fixed Interest-bearing Debt and Preference Share Capital along with Equity Share Capital is called as financial leverage. The above description of the different methods may sound somewhat intimidating. Fortunately, all three methods are nothing more than weighted averages that can easily be calculated using a financial calculator or spreadsheet software. This example excludes real-life factors such as interest payments. If the home’s value increases 10% to $550,000, your gains would be magnified to 50%.
Calculate
Consideration of the combined effects of operating and financial leverage magnifies the effects of leverage on earnings per share. The two leverage factors together increase the dispersion and rid; of forecasting earnings per share. This type of analysis is not limited to debt or common stock financing. We can also utilize it in analyzing a combination of debt and equity financing alternatives in order to determine the effect of the various combinations on the earnings per share of the firm.
Operating leverage defines the overall position of the fixed operating cost. Knowing the weight of the composite and fiber for a given area, we can calculate the weight of resin . These calculations are most easily done for a specific area of a laminate – say one square meter – and then used for specific areas once they are generalized. To calculate the V_fiber, and therefore the V_resin (which is 1 – V_fiber) we first need to know the weight of the fiber in the unit of laminate we are evaluating. On the other hand, a low DCL means the company is having a low risk. Even there is a change in sales, the EPS will not get a huge impact due to a lower sensitivity.
To calculate this ratio, find the company’searnings before interest and taxes, then divide by the interest expense of long-term debts. Use pre-tax earnings because interest is tax-deductible; the full amount of earnings can eventually be used to pay interest. Thedebt-to-EBITDAleverage ratio measures a company’s ability to pay off its incurred debt. Commonly used by credit agencies, this ratio determines the probability of defaulting on issued debt. Since oil and gas companies typically have a lot of debt on their balance sheets, this ratio is useful in determining how many years of EBITDA would be required to pay back all the debt.

Because interest is an expense which is deductible before tax, it acts as a tax shield for the corporation. Any firm that is considering the use of debt or preferred stock in its capital structure must weigh the impact that the increased leverage will have on earnings per share. Management’s object in seeking these funds is to increase the earnings per share. The example below illustrates how debt and stock financing affect this aspect of a company’s financial position. The percentage change in a firm’s earning per share results from one percent change in sales.
Degree of Financial Leverage
Although debt is not specifically referenced in the formula, it is an underlying factor given that total assets includes debt. It is helpful to know how EPS would change with a change in operating profit. It is concerned with fixed Financial Costs or debt capital of a company. When comparing two or more companies, the company with the highest DOL is the company the profits of which are most “sensitive” to changes in sales. Financial manager uses the operating leverage to identify the items of assets side of the Balance. You are required to compare the sensitivity of earnings of the two companies for a 25% change in the level of their current Assets.
What is Leverage?
The DCL formula summarizes the effects that the combined degree of operating leverage and degree of financial leverage have on a company’s earnings per share, based on a given change in shares. A company’s operating leverage is the relationship between a company’s fixed costs and variable costs. Financial leverage refers to the extent of fixed cost debt capital used by a firm in order to maximize the earning of shareholder, financial leverage is also termed as “trading on equity”.
The restrictions are imposed because of increased risk and to maintain a balance in capital structure of the firm. Before going to workout the problems, there is a need to know how to compute the earnings available to the equity shareholders from the sales revenue. The following format clearly gives a picture about the calculation of earnings available to the ordinary shareholders. Financial risk is the risk of not being able to meet fixed financial obligations like payment of interest on debt.
The Debt-To-EBITDA Leverage Ratio
EBIT Earnings before interest and tax refers to the company’s operating profit that is acquired after deducting all the expenses except the interest and tax expenses from the revenue. It denotes the organization’s profit from business operations while excluding all taxes and costs of capital. If the firm obtains fixed cost funds at a higher cost, then the earnings from those assets, the earning per share and return on equity capital will decrease. The degree of total leverage can also be referred to as the “degree of combined leverage” because it considers the effects of both operating leverage and financial leverage. The higher the ratio, the greater the risk that the company will default on its debt obligations.
Unbalanced and asymmetrical laminates will tend to bend out of the plane of the panel when loaded. These “coupling” issues can lead to extension bending and twisting – which is fine, but requires additional analysis. If you get into “Classical Laminate Theory” you will see that the ABD matrix ties the loads and strains by way of extension, composite leverage formula bending and coupling of the two. Balanced and symmetrical laminates allow you to “zero out” whole swaths of these parameters because the loads result only in in-plane strain. These are linear and with the exception on very thin laminates, should remain quite accurate. You could estimate that 10,000g of carbon at 0.5FVF would be 11mm thick.
By calculating cl, finance managers can make more precise decisions with regards to the company’s overall risk. Additionally, cl can help managers identify any potential issues with the company’s capital structure. The percentage change in sales amounts to 10% , whereas the percentage change in EPS amounts to approximately 16.67% (1/6 x 100). Thus, every 1% change in the sales level results in a 1.67% change in EPS. Taking the percentage of sales at break-even point; it will reach at 33.3% of sales in situation A, 50% in situation B and 62.5% in situation C.
A low degree of financial leverage also gives a company more flexibility in how it uses its cash flow. The higher the DOL, the more sensitive EBIT is to changes in sales. A high DOL can be advantageous because it means that a company can generate a large amount of EBIT with only a small increase in sales. However, it can also be risky because a small decrease in sales can result in a large decrease in EBIT.
A high degree of operating leverage together with a high degree of financial leverage makes the position of the firm very risky. High operating leverage results from employing the assets for which it has to pay higher fixed costs and high financial leverage results from the use of large amount of debt capital. High degree of operating leverage indicates higher degree of risk. It is good when revenues are rising and bad when they are falling. Operating risk is the risk of the firm not being able to cover its fixed operating costs. The larger the magnitude, the larger the volume of sales required to cover all fixed costs.
